Objective-C语法之基本数据类型
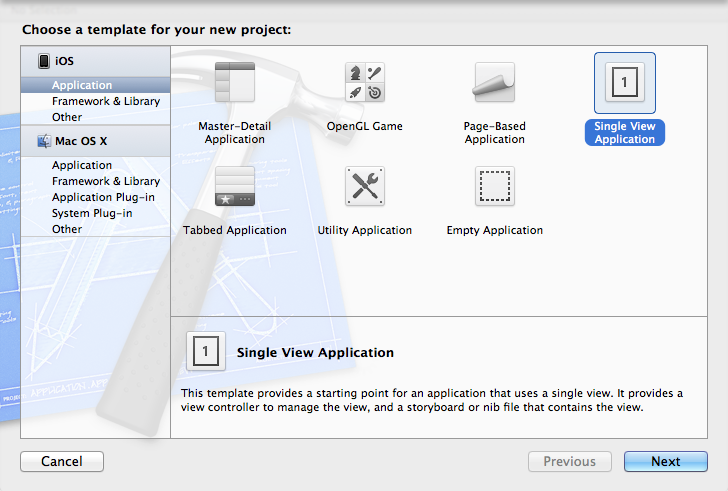
1、新建项目
为了方便,我们新建一个Single View Application 。
输入项目名称 BaseType

Product Name: 指产品名称 ,类似于项目名称。
Company Identifier: 公司标识符,一般命名规则为 “com.公司名”
Bundle Identifier: 指包标识符,用于唯一标识应用程序,默认会根据公司标识符和产品名来组合生成
Device Family: 指该应用支持的设备类型,共三个选项:iPhone、iPad、Universal(即iPhone、iPad通用)
Include Unite Tests: 是否包含单元测试代码模板,如果勾选,Xcode会帮助生成单元测试代码模板
在项目里找到,ViewController.m 为了方便演示,在界面启动时,我们加入测试代码
2 、C语言的基本数据类型长度
NSLog(@"The size of an int is: %lu bytes.",sizeof(int)); NSLog(@"The size of a short int is: %lu bytes.",sizeof(short int)); NSLog(@"The size of a long int is: %lu bytes.",sizeof(long int)); NSLog(@"The size of a char is: %lu bytes.",sizeof(char)); NSLog(@"The size of a float is: %lu bytes.",sizeof(float)); NSLog(@"The size of a double is: %lu bytes.",sizeof(double)); NSLog(@"The size of a bool is: %lu bytes.",sizeof(bool)); // Do any additional setup after loading the view,结果:
2012-06-13 13:55:46.726 BaseType[3032:f803] The size of an int is: 4 bytes. 2012-06-13 13:55:46.726 BaseType[3032:f803] The size of a short int is: 2 bytes. 2012-06-13 13:55:46.727 BaseType[3032:f803] The size of a long int is: 4 bytes. 2012-06-13 13:55:46.731 BaseType[3032:f803] The size of a char is: 1 bytes. 2012-06-13 13:55:46.732 BaseType[3032:f803] The size of a float is: 4 bytes. 2012-06-13 13:55:46.733 BaseType[3032:f803] The size of a double is: 8 bytes. 2012-06-13 13:55:46.733 BaseType[3032:f803] The size of a bool is: 1 bytes.
3、格式化输出数据
//整型 int integerType = 5; //浮点型 float floatType = 3.1415; //双浮点型 double doubleType = 2.2033; //短整型 short int shortType = 200; //长整型 long long int longlongType = 7758123456767L; //c语言字符串 char * cstring = "this is a string!"; //整型 NSLog(@"The value of integerType = %d",integerType); //浮点型 NSLog(@"The value of floatType = %.2f",floatType); //双浮点型 NSLog(@"The value of doubleType = %e",doubleType); //短整型 NSLog(@"The value of shortType = %hi",shortType); //长整型 NSLog(@"The value of longlongType = %lli",longlongType); //c语言字符串 NSLog(@"The value of cstring = %s",cstring);
结果:
2012-06-13 14:06:18.757 BaseType[3215:f803] The value of integerType = 5 2012-06-13 14:06:18.757 BaseType[3215:f803] The value of floatType = 3.14 2012-06-13 14:06:18.758 BaseType[3215:f803] The value of doubleType = 2.203300e+00 2012-06-13 14:06:18.758 BaseType[3215:f803] The value of shortType = 200 2012-06-13 14:06:18.758 BaseType[3215:f803] The value of longlongType = 7758123456767 2012-06-13 14:06:18.758 BaseType[3215:f803] The value of cstring = this is a string!
5、 int,NSInteger,NSUInteger,NSNumber
1.当需要使用int类型的变量的时候,可以像写C的程序一样,用int,也可以用NSInteger,但更推荐使用NSInteger,因为这样就不用考虑设备是32位的还是64位的。
2.NSUInteger是无符号的,即没有负数,NSInteger是有符号的。
3.有人说既然都有了NSInteger等这些基础类型了为什么还要有NSNumber?它们的功能当然是不同的。
NSInteger是基础类型,但是NSNumber是一个类。如果想要在NSMutableArray里存储一个数值,直接用NSInteger是不行的,比如在一个NSMutableArray里面这样用:
NSMutableArray *array = [[NSMutableArray alloc]init]; [array addObject:[NSNumber numberWithInt:88]];

这样是会引发编译错误的,因为NSMutableArray里面放的需要是一个类,但‘88’不是类。
Cocoa提供了NSNumber类来包装(即以对象形式实现)基本数据类型。
例如以下创建方法:
+ (NSNumber *) numberWithChar: (char) value;
+ (NSNumber *) numberWithInt: (int) value;
+ (NSNumber *) numberWithFloat: (float) value;
+ (NSNumber *) numberWithBool: (BOOL) value;
将基本类型数据封装到NSNumber中后,就可以通过下面的实例方法重新获取它:
- (char) charValue;
- (int) intValue;
- (float) floatValue;
- (BOOL) boolValue;
- (NSString *) stringValue;
例子:
NSNumber *num = [NSNumber numberWithInt:88]; NSInteger integer = [num intValue];
5、NSString与NSInteger的相互转换
NSInteger integerNumber = 888; NSString * string = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d",integerNumber]; NSLog(@"string is %@", string);
integer = [string intValue]; NSLog(@"integer is%d", integerNumber);
char float等类型一样可以转换
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/totogo2010/article/details/7655908